People check phones over 100 times daily. How annoying would it be to get the cables every time we go online? Wi-Fi changed everything forever. It connects us to the Internet without wires.
Wi-Fi is also known as Wireless Fidelity. It uses radio waves for wireless networks. Devices like laptops, smartphones, and tablets can connect to the internet wirelessly without cables. Wi-Fi routers act like central hubs. They send out radio waves and help your devices connect to the internet.
Wi-Fi works by using radio waves. These unseen waves are part of a spectrum. They convey data by moving at particular rates. Wi-Fi sends data using specific radio waves, like colored lights with different wavelengths.
This blog will teach how Wi-Fi signals work and how radio waves function. We will also see how wifi signals are broadcasted. So, let’s get started.
What are Radio Waves?
Radio waves live in an enormous spectrum of invisible waves. From radio waves to gamma rays, the electromagnetic spectrum surrounds us.
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies. They carry signals for radio broadcasts, televisions, and even Wi-Fi. If this sounds too technical, don’t worry we will cover this part further in the article.
Properties of Radio Waves
To understand wifi signal transmission, we need to first understand radio waves. Here are some of the main properties of the radio waves:
- Frequency: Frequency measures how often the wave oscillates per second. It is measured in units known as Hertz (Hz). Higher frequencies mean shorter wavelengths. It results in faster data transmission.
- Wavelength: Wavelength is the space between wave peaks. It has an inverse relationship with frequency: higher frequencies lead to shorter wavelengths.
- Amplitude: Amplitude refers to the wave’s intensity or height. For Wi-Fi, strong amplitude means a powerful signal that travels far. Amplitude is linked to frequency – higher frequencies mean shorter wavelengths.
How Data Is Converted To Radio Waves?
Our digital data consists of ones and zeros. To transmit it wirelessly, the data must be converted to radio waves. This conversion happens through modulation. Wi-Fi uses two methods: Amplitude Modulation (AM) and Frequency Modulation (FM).
- Amplitude Modulation (AM): AM changes the radio wave’s strength to show data. High amplitude equals one, low amplitude equals zero. You can understand this with the help of a radio signal’s volume going up and down to send data.
- Frequency Modulation (FM): FM changes the pitch of the radio wave to transmit information. A higher frequency equals one, and a lower frequency is zero.
How Does Wi-Fi Router Work?
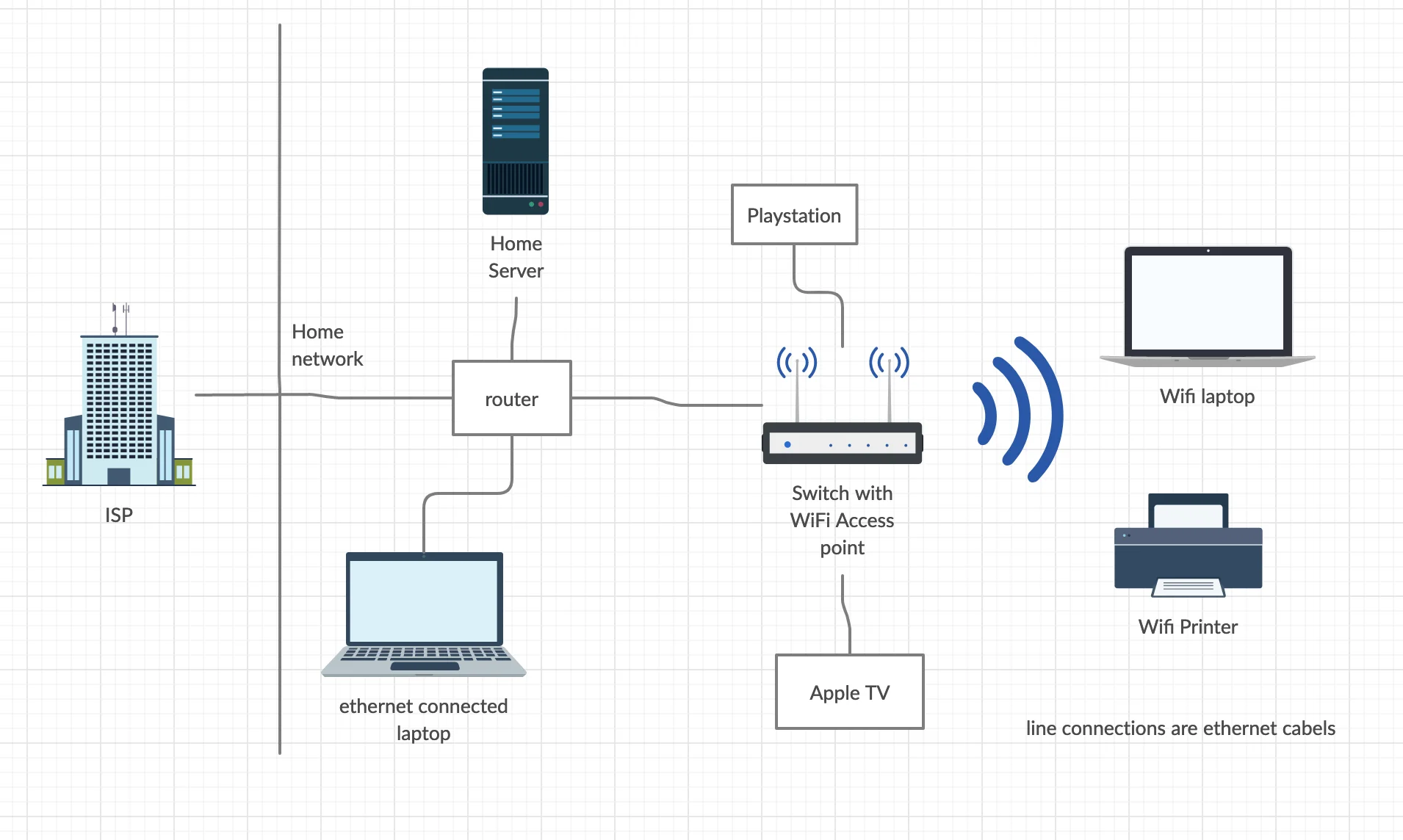
Image Source: SuperUser.com
Wi-fi router plays an important role in broadcasting wi-fi signals. Let’s have a closer look at it:
Components of a Wi-Fi Router
Without a wifi router, we can’t imagine having a wireless connection. Wi-Fi routers are usually compact in size. Inside this compact form, we have its advanced parts. Let’s have a look at them:
- Antenna: The antenna transmits and receives radio signals. An omnidirectional antenna sends signals everywhere. It is similar to a lighthouse’s rotating light. Directional beams target signals like spotlights do.
- Transmitter: The transmitter converts device data into radio waves through modulation, broadcasting via antenna.
- Receiver: The receiver catches radio waves from devices. It changes them into data packets and links to the internet via a wired connection.
- Processing Unit: The CPU in the router handles data, encryption, and device-internet communication.
Types of Antennas
Antennas vary in strength and direction. Let’s have a look at their different types:
- Omnidirectional antennas: Omnidirectional antennas spread Wi-Fi signals equally in all directions. They are like a lighthouse with a rotating light. This is good for big areas. But the signal gets weaker as it spreads.
- Directional antennas: Directional antennas focus the Wi-Fi signal like a spotlight. This provides a stronger signal in specific spots.
Types of Frequencies
Wi-Fi routers work on two main frequency bands – 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. They have different capabilities. Let’s understand them closely:
- 2.4 GHz: The 2.4 GHz band has a better range and can go through walls easily. The older 2.4 GHz band has better coverage but can get slow due to other devices using the same frequency. For high-data tasks like watching videos or gaming near the router, the 2.4 GHz band works well. It covers larger areas and goes through walls easily.
- 5 GHz: The newer 5 GHz band is faster but has a shorter range and may not go through walls easily. The 5 GHz band provides faster speeds but covers a smaller area. For tasks that require lots of data, such as streaming videos or gaming nearby, the 5 GHz band can be the best choice for you.
Security Measures
Security is important for any wireless network. Wi-Fi routers use security methods like WPA and WPA2 to protect data. This makes it hard for devices not allowed to access your network and steal sensitive information. You should always turn on strong encryption on your router. You should also use a unique password to protect your Wi-Fi.
How Are Wi-Fi Signals Broadcast?
Communication between Wi-Fi devices and routers is a two-way process. When connecting to a network, your device sends a request with its info (like MAC address). The router receives this information, checks its security, and if everything is okay, it gives access to the wifi device.
Connection Establishment Between Device and Wi-Fi Router
After the device is verified, it connects to the network. Your device searches for Wi-Fi networks by sending signals. Your device sends signals to nearby routers to indicate the type of network it seeks.
Routers with their SSIDs activated advertise network details and security settings. Once you choose a network, your device begins communication with the router. It verifies the encryption method and exchanges security keys. After the verification, your device connects to the network.
How Does The Data Move?
Data is not sent continuously. Instead, it is divided into small parts known as packets. Packets hold the web data you need. They include info on where it comes from, where it is going. It also has codes to spot any errors. The router efficiently directs data packets between your devices and the internet.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Yes, walls can seriously hamper Wi-Fi signals. Let’s have a look at types of walls:
Thin materials like drywall, plywood, and glass generally let Wi-Fi signals slip through relatively easily. It has very minimal weakening effects.
But thicker materials, such as concrete walls, really dampen Wi-Fi signals significantly. Even brick walls and thick plaster complete with metal can cause notable signal loss.
he answer depends on your needs and priorities. Let’s see how:
5 GHz:
Pros: Way faster speeds, perfect for high-bandwidth tasks like streaming ultra HD videos, online gaming, and downloading huge files.
Cons: Limited range, struggles to pass through walls.
2.4 GHz:
Pros: Superior range, can pass through walls and obstacles more easily for wider coverage.
Con: Slower speeds than 5 GHz, more prone to congestion from other devices using the same band.
Various factors impact your Wi-Fi performance. You can try these troubleshooting tips:
1. Router Placement: Position the router centrally with minimal obstructions like walls, and electronics.
2. Minimize Interference: Identify, and relocate devices interfering with Wi-Fi signal e.g., cordless phones, Bluetooth speakers, microwaves.
3. Channel Change: Use the Wi-Fi analyzer app, and switch to less congested channel in densely populated areas.
4. Upgrade Equipment: Older wifi routers may lack newer Wi-Fi standards, and struggle while you use multiple devices. So it is better to upgrade to the latest standard (Wi-Fi 6) for better speed and capacity.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi is a technology that utilizes radio waves to provide internet connectivity. Wifi routers broadcast these signals that your devices can access. Several factors can influence the range of the signals.
You should position the router strategically in your house. This will minimize interference. You can also upgrade wifi equipment to improve Wi-Fi performance.
Ready to upgrade your Wi-Fi experience? We offer comprehensive Wi-Fi solutions for businesses and villas in the UAE. From extending your range to optimizing your network, we’ve got you covered. Contact us today to explore our complete Wi-Fi solutions.